Applications of intraoperative ultrasound in the treatment of complicated cases of acute and chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer – own experience
Grzegorz Ćwik, Michał Solecki, Grzegorz Wallner
 Affiliation and address for correspondence
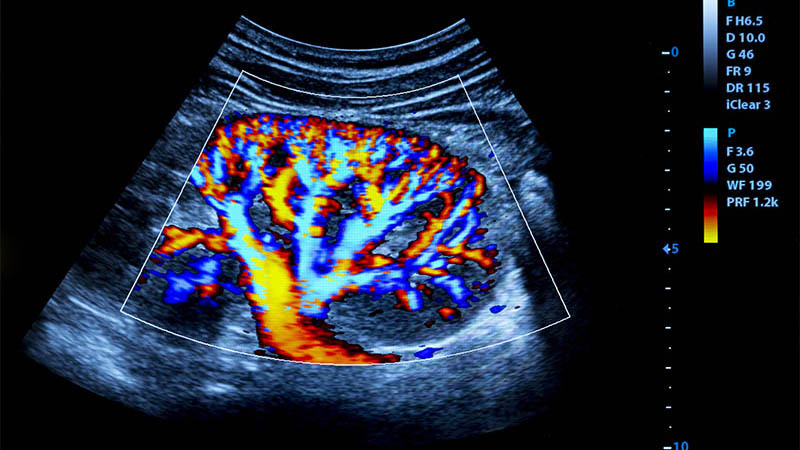
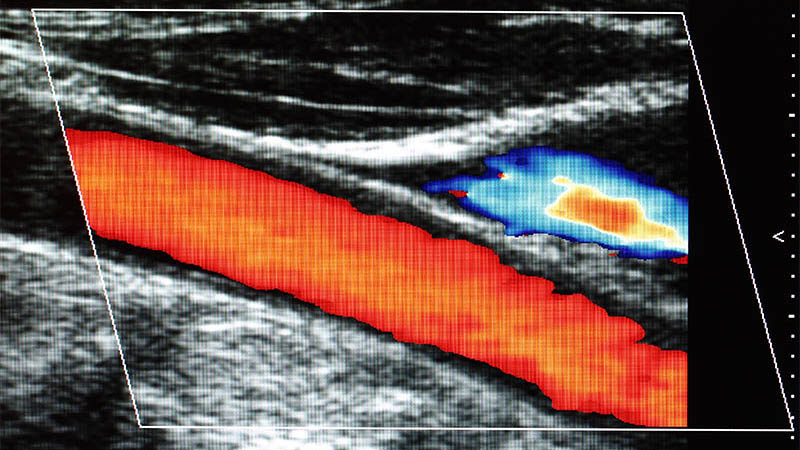
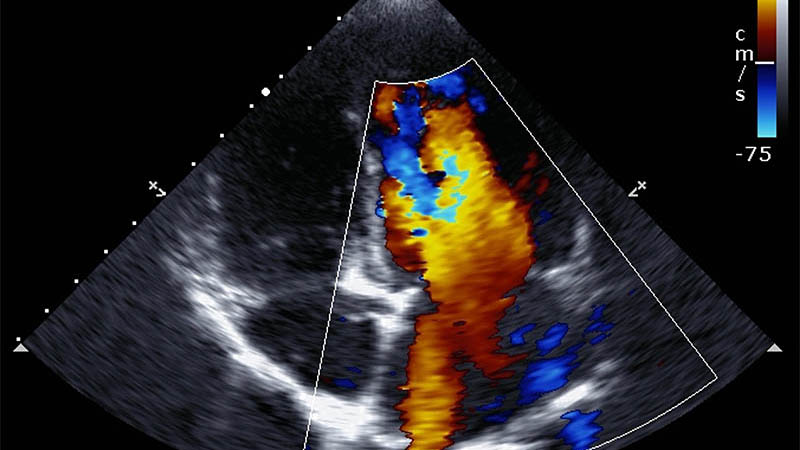
Affiliation and address for correspondenceBoth acute and chronic inflammation of the pancreas often lead to complications that nowadays can be resolved using endoscopic and surgical procedures. In many cases, intraoperative ultrasound examination (IOUS) enables correct assessment of the extent of the lesion, and allows for safe surgery, while also shortening its length. Aim of the research: At the authors' clinic, intraoperative ultrasound is performed in daily practice. In this paper, we try to share our experiences in the application of this particular imaging technique. Research sample and methodology: Intraoperative examination conducted by a surgeon who has assessed the patient prior to surgery, which enabled the surgeon to verify the initial diagnosis. The material presented in this paper includes 145 IOUS procedures performed during laparotomy due to lesions of the pancreas, 57 of which were carried out in cases of inflammatory process. Results and conclusions: IOUS is a reliable examination tool in the evaluation of acute inflammatory lesions in the pancreas, especially during the surgery of chronic, symptomatic inflammation of the organ. The procedure allows for a correct determination of the necessary scope of the planned surgery. The examination allows for the differentiation between cystic lesions and tumors of cystic nature, dictates the correct strategy for draining, as well as validates the indications for the lesion's surgical removal. IOUS also allows the estimation of place and scope of drainage procedures in cases of overpressure in the pancreatic ducts caused by calcification of the parenchyma or choledocholitiasis in chronic pancreatitis. In pancreatic cancer, IOUS provides a verification of the local extent of tumor-like lesions, allowing for the assessment of pancreatic and lymph nodes metastasis, and indicating the presence of distant and local metastases, including the liver. IOUS significantly improves the effectiveness of intraoperative BAC aspiration or drainage of fluid reservoirs.