Intra-abdominal fat. Part III. Neoplasms lesions of the adipose tissue
Andrzej Smereczyński, Katarzyna Kołaczyk, Elżbieta Bernatowicz
 Affiliation and address for correspondence
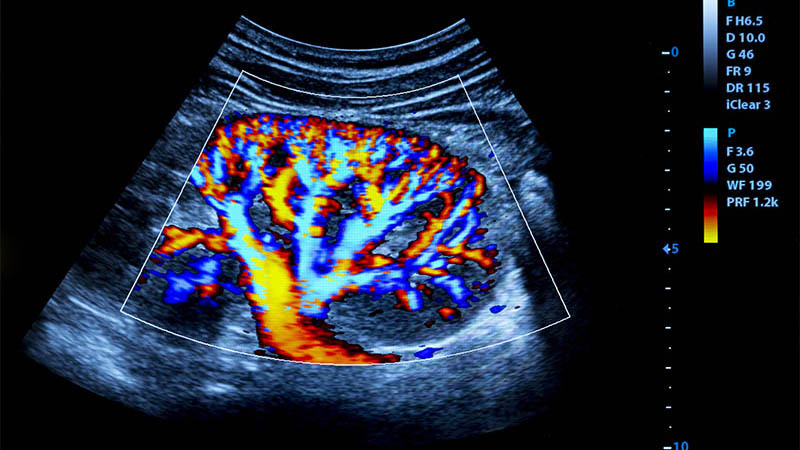
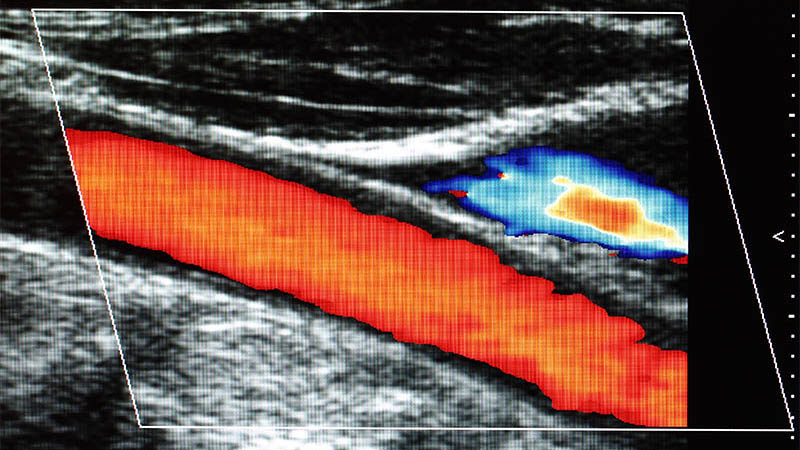
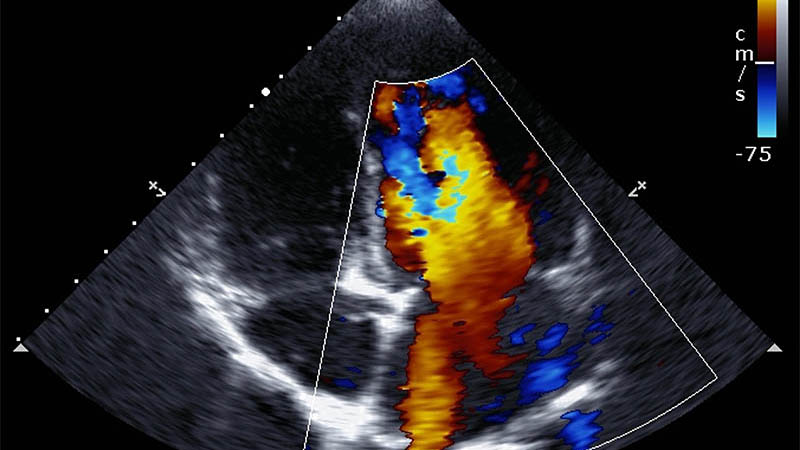
Affiliation and address for correspondenceThis article focuses on various cancerous lesions that are found beyond organs in the intra-abdominal fat and can be visualized with ultrasonography. These lesions are divided into five groups. The first group includes primary benign tumors containing adipocytes, such as lipoma, lipoblastoma, hibernoma and other lesions with an adipose tissue component, such as myolipoma, angiomyolipoma, myelolipoma and teratoma. The second group comprises primary malignant adipocytecontaining tumors, including liposarcoma and immature teratoma. The third group contains primary benign tumors without an adipocyte component that are located in intra-abdominal fat. This is a numerous group of lesions represented by cystic and solid tumors. The fourth group encompasses primary malignant tumors without an adipocyte component that are located in intra-abdominal fat. These are rare lesions associated mainly with sarcomas: fibrosarcoma, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, hemangiopericytoma and leiomyosarcoma. An epithelioid tumor at this site is mesothelioma. The last but not least group includes secondary malignant tumors without an adipocyte component located in intra-abdominal fat. This is the most numerous group with prevailing carcinoma foci. For each of these groups, the authors present ultrasound features of individual lesions and discuss their differential diagnosis. In the vast majority of cases, the material for cytological and histological analysis can be obtained during ultrasound-guided procedures. This is the advantage of this imaging modality.