Evaluation of parenchymal vascularity of the thyroid gland with vascularization index by color superb microvascular imaging in patients with Graves’ disease
Abidin Kılınçer1, Mehmet Sedat Durmaz1, Cem Onur Kıraç2, Süleyman Baldane2, Fatih Ateş1, Abdüssamet Batur1
 Affiliation and address for correspondence
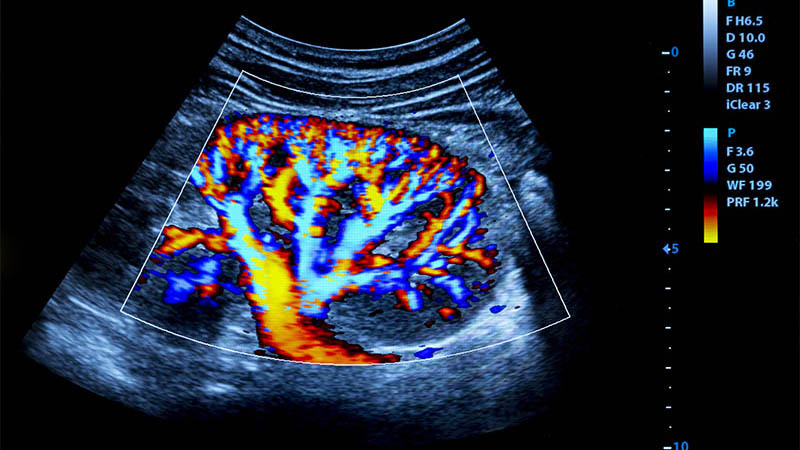
Affiliation and address for correspondenceAim of the study: To determine the parenchymal vascularity of the thyroid gland with color superb microvascular imaging in patients with Graves’ disease, and compare the vascularization index values with healthy subjects. Materials and methods: The thyroid glands of 37 patients whose laboratory and clinical findings were consistent with Graves’ disease, and 40 asymptomatic subjects with normal laboratory values, were examined using color superb microvascular imaging. Measurements of the vascularization index were performed with a free region of interest which was drawn along the outer margin of the gland on the color superb microvascular imaging mode. The vascularization index values obtained in the Graves’ disease and control groups were compared. A correlation analysis was performed between the vascularization index values and laboratory and grayscale US parameters. Results: The median vascularization index value of the thyroid parenchyma in patients with Graves’ disease was significantly higher than in the asymptomatic group [median (min–max); 12 (2.3–32.1) vs 5.04 (1.1–10.8), p <0.001]. When the cutoff value of the vascularization index is determined as 6.3, Graves’ disease can be diagnosed with 83.8% sensitivity and 70% specificity. Conclusions: The vascularization index obtained with color superb microvascular imaging can be a quantitative indicator of parenchymal vascularity in the diagnosis of Graves’ disease, and serve as a supportive tool.